Highlights
- Kotlin Multiplatform lets developers maintain a single shared codebase that compiles to native performance on Android, iOS, desktop, and web — cutting redundancy without sacrificing native capabilities.
- From sharing core business logic to building full cross-platform UIs with Compose Multiplatform, KMP adapts to every project’s architecture and platform.
- Unlike Flutter or React Native, KMP lets engineers integrate native APIs directly and mix shared and platform-specific code for true development flexibility.
- Adopted by companies like Netflix, Autodesk, and Philips, Kotlin Multiplatform accelerates development, enhances collaboration, and reduces time-to-market for cross-platform solutions.
What is Kotlin Multiplatform?
In software development's dynamic landscape, Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) stands out, revolutionizing cross-platform projects. It's a game-changer, minimizing the effort spent on duplicating code across different platforms.
At its core, KMP merges native programming flexibility with a unified codebase, dramatically reducing development time. With KMP, a single code base effortlessly spans iOS, Android, mac OS, Windows, Linux, and beyond, promising true cross-platform compatibility in a nutshell.
How does Kotlin Multiplatform work?
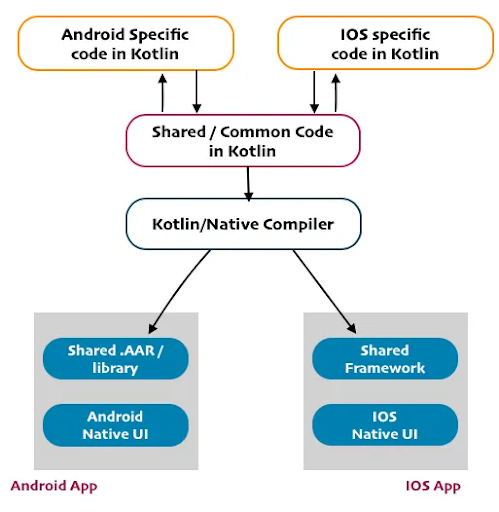
KMP, the code maestro, seamlessly orchestrates harmony across Android and iOS. Starting with shared business logic, KMP transforms it into a universal language for both platforms.
Android: JVM ballet
- KMP choreographs a JVM ballet for Android.
- Code transforms into Java bytecode, harmonizing with the Android environment effortlessly.
iOS: Native symphony
- For iOS, KMP conducts a native symphony.
- Code converts into native machine language, ensuring optimal performance without compromise on iPhones and iPads.
Kotlin common code
The Core Concept: Kotlin Common Code is the linchpin of Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP), embodying shared business logic across platforms.
Platform-specific compilers:
Kotlin/JVM: Transforms common code into Java bytecode for seamless integration with the Android ecosystem.
Kotlin/JavaScript: Converts code into JavaScript, enabling cross-platform compatibility for web development.
Kotlin/Native: Navigate non-JVM environments by converting code into native machine code, expanding compatibility.
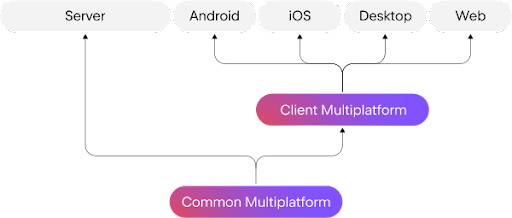
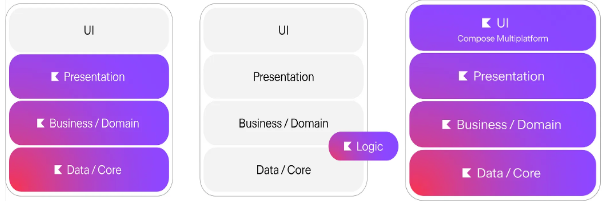
Different code-sharing approaches with KMP
In Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP), flexibility reigns supreme. Code sharing ranges from minimal logic to complete UIs via Compose Multiplatform:
Minimalist sharing:
- Choose specific logic for sharing.
- Ideal for preserving platform uniqueness.
Intermediate sharing:
- Share a substantial code portion.
- Balances efficiency with platform specifics.
Compose Multiplatform:
- Unify logic and entire UI code.
- Revolutionizes the cross-platform experience.
Choose your KMP approach—minimalist, intermediate, or Compose Multiplatform. Stay tuned for real-world examples, diving into the dynamic realm of cross-platform development!
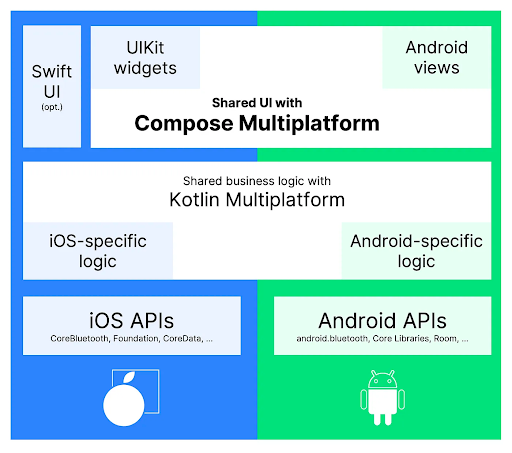
Kotlin Multiplatform vs. other cross-platform approaches
In the cross-platform arena, Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) stands out. It provides a single code base for iOS and Android, akin to other approaches, but with unmatched flexibility:
Platform-specific flexibility:
- KMP allows platform-specific code for unparalleled adaptability.
Liberation from ecosystem lock-in:
- Unlike Flutter or React Native, KMP frees developers from ecosystem constraints.
- Write native code anywhere in the application.
The Kotlin Multiplatform advantage:
- Freedom to leverage framework-supported features or seamlessly integrate native code.
- Unparalleled adaptability without compromising cross-platform efficiency.
Advantages of Kotlin Multiplatform
In the programming world, Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) stands as an efficient game-changer for developers:
Robust support:
Widely adopted by organizations.
- Google's endorsement cements its role as the preferred Android language.
- Thriving community support encourages collaboration.
Efficient code:
- Eliminates redundancy in cross-platform code creation.
- Swift common code sharing minimizes development time.
- Features like interoperability ensure speed without compromising on native platforms.
Accelerated development:
- Code sharing equals swift and efficient development.
- Kotlin's attributes—null safety, IDE support, and Java interoperability—streamline complexity for faster results.
Unified language for all:
- Breaks free from cross-platform tool limitations.
- Utilizes native capabilities on iOS and Android seamlessly.
- Smooth transition: Android apps adapt to iOS devices without extensive code modifications.
Companies who use Kotlin Multiplatform
The impact of Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) resonates across industry giants:
Netflix: elevating UI
- Reimagined Android UI player with KMP.
- Seamless, cross-platform UI for an enhanced streaming experience.
Autodesk: bridging platforms
- Embraces KMP's native compatibility for iOS and Android.
- Streamlines cross-platform development without Java interface complexities.
VMware: The go-to framework
- Cloud computing giant selects KMP for cross-platform mobile apps.
- Optimal choice for streamlined development.
Trello: Project management simplified
- Adopts Kotlin for Android app development.
- Smooth transition facilitated by Kotlin's Java interoperability.
Philips: Accelerating innovation
- Experience speed with KMP in implementing new features.
- Fosters collaboration between Android and iOS developers.
IceRock: Crafting versatile solutions
- Relies on KMP Mobile for diverse industry applications.
- Empowers seamless development for mobile and backend solutions.
Kotlin Multiplatform: One codebase, infinite platforms
In the journey through the realms of Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP), we've navigated its intricate workings, explored diverse code-sharing approaches, and witnessed its adoption by industry leaders. As the curtain falls on this exploration, it's evident that KMP isn't just a technology; it's a transformative force reshaping the landscape of cross-platform development.
In conclusion, Kotlin Multiplatform isn't just a tool; it's a catalyst for change. As it disrupts traditional norms, KMP opens doors to a future where developers wield the power to code efficiently, collaboratively, and without constraints. The journey with KMP doesn't end here; it marks the beginning of a new era in cross-platform development, where innovation knows no bounds.
Embark on this transformative journey with Kotlin Multiplatform—where the language of code transcends platforms, and the future of development unfolds with boundless possibilities.
From idea to impact, build what’s next with KeyValue. Let’s shape the future of technology together. Connect with us.
FAQs
- What is Kotlin Multiplatform used for?
Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) is used to share code across multiple platforms — Android, iOS, desktop, web, and backend — from a single Kotlin codebase. It lets developers write common business logic once and compile it into platform-native code, reducing duplication while maintaining native performance and flexibility.
- What is a codebase?
A codebase is the entire set of source code and related assets that make up a software project. It includes application logic, configuration files, libraries, and build scripts, all typically managed in a version control system. It serves as the authoritative source for developing, maintaining, and deploying the software.
- How does Kotlin Multiplatform differ from Flutter and React Native?
Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) focuses on sharing business logic while keeping native UI and performance, letting developers use platform-specific APIs directly. Flutter and React Native use a single UI framework for all platforms, offering faster UI development but less native flexibility and integration.
- Does Netflix use Kotlin Multiplatform?
Yes, Netflix uses Kotlin, including Kotlin Multiplatform, to build and optimize its Android and cross-platform apps—enhancing performance, code sharing, and development efficiency.
- Why should developers learn Kotlin Multiplatform now?
Developers should learn Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) because it offers a modern, flexible approach to cross-platform development — sharing code across Android, iOS, web, and desktop without losing native performance. With strong JetBrains and Google support and growing industry adoption, KMP skills are becoming a key advantage in building scalable, future-ready apps.
- Can Kotlin Multiplatform be used for production apps?
Yes. Kotlin Multiplatform is production-ready and used by companies like Netflix, Philips, and Autodesk. It enables shared logic, native performance, and seamless integration with existing Android and iOS projects — making it ideal for scalable, real-world apps.
- What’s the difference between Kotlin/JVM, Kotlin/JS, and Kotlin/Native?
Kotlin/JVM compiles code to Java bytecode for Android and server apps on the JVM. Kotlin/JS compiles to JavaScript, enabling Kotlin for web development. Kotlin/Native compiles to machine code, running on non-JVM platforms like iOS, macOS, and Linux. Each targets a unique runtime, making Kotlin truly cross-platform.

