Highlights
- Learn how to create a product roadmap that aligns vision, goals, and execution.
- Understand the key elements that make a software product roadmap effective.
- Explore agile vs waterfall roadmaps and when to use each.
What is a product roadmap, and why does it matter?
In today’s world, where teams collaborate across borders and work on shared digital platforms, one of the biggest challenges for product managers is communicating product strategy clearly. Misalignment across stakeholders slows execution and often leads to rework.
A product roadmap solves this problem. It provides a structured, visual summary of the product vision, direction, and major initiatives over time. Whether the product is a system, service, or tool, the roadmap acts as a single source of truth that keeps the entire team aligned.
A well-crafted roadmap not only outlines what is being built but also helps the team understand why those decisions are made, how the product evolves, and how it solves real user problems.
Why is a product roadmap so critical for product teams?
A roadmap ensures that everyone working on the product is aligned on expected outcomes and future direction. It connects the product vision with actionable goals, helping teams rally around a shared understanding of success.
Since the product roadmap is accessible to everyone regardless of role, it acts as a strategic document for tracking progress through the product life cycle. It reduces confusion, keeps teams on the same page, and enables healthy feedback loops with business, marketing, engineering, design, and leadership.
Because a roadmap covers vision, goals, features, and timelines, it also helps teams identify gaps early in the development process. This strengthens planning and improves execution predictability.
How to create a product roadmap?
1. Define your product vision
Start with the big picture. What problem are you solving and why? A strong vision acts as the North Star for the roadmap.
2. Set clear goals
Break the vision into measurable milestones such as user growth, revenue goals, adoption rates, or feature releases.
3. Understand your users and stakeholders
Collect insights from end-users, teams, and market research. This ensures your priorities reflect real needs.
4. Prioritize features the right way
Use frameworks like MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won't-have) or RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort) to rank features.
5. Choose your roadmap format and timeline
Decide whether you are building a product roadmap that is time-based, theme-based, or outcome-based. Different teams benefit from different structures.
6. Visualize your roadmap using the right tools
Platforms like Trello, Jira, Aha!, and , help you map initiatives, dependencies, and timelines clearly.
7. Share and get feedback
Once your roadmap is ready, share it with stakeholders. Identify gaps, refine priorities, and confirm alignment.
8. Keep the roadmap flexible
A good software product roadmap evolves continuously to reflect changing markets, user behaviour, and business needs.
A successful roadmap balances ambition and realism, giving the team clarity without locking them into rigid commitments.
What are the key features of a product roadmap?
The following key features make up a product roadmap, but they're not limited to them.
- A FEATURE is the basic unit of the product that is part of the functionality or which can be part of the 3rd party application.
- To understand the progress of development, STATUS MARKERS are used.
- To derive data-driven goals from a product roadmap, different types of METRICS are used.
- The PRODUCT VISION defines the future outcome of a product.
- The roadmap consists of TIME-FRAMES which define the time periods and specific dates aligned with the product goals.
- The product roadmap consists of GOALS which define the objectives that need to be done within a defined time period.
- Once the goals and product vision are defined, it's the PRODUCT STRATEGY that defines the plan of execution.
- The features and tasks are categorized into EPICS
- Features are prioritized based on different aspects and PRIORITY will help the team understand the features' importance.
A product roadmap becomes complete when the product vision and its strategy are defined by goals that are based on a time frame aligned with the product life cycle. It evolves based on customer needs and market trends. With the help of a product roadmap, the team can identify high-priority features and business requirements and communicate expectations among the team.
What are the different types of product roadmaps?
Internal vs external roadmaps
- Internal roadmaps serve specific teams such as engineering, marketing, or sales.
- Engineering = detailed milestones, sprints, and on the release plans
- Sales = feature benefits and customer-facing commitments
- External roadmaps are simple, visual, and focused on upcoming value for users and prospects.
Agile vs waterfall product roadmaps
Both styles support different product development environments:
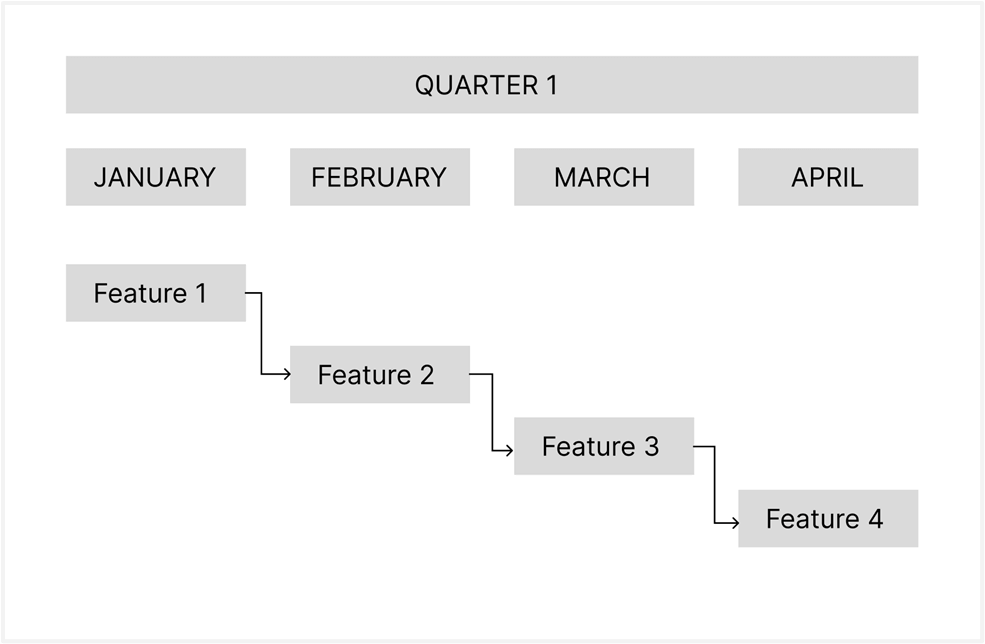
Waterfall roadmaps
Waterfall roadmaps suit long-term planning where tasks are sequential and interdependent. Each task begins only after the previous one finishes, making timelines strict and predictable.
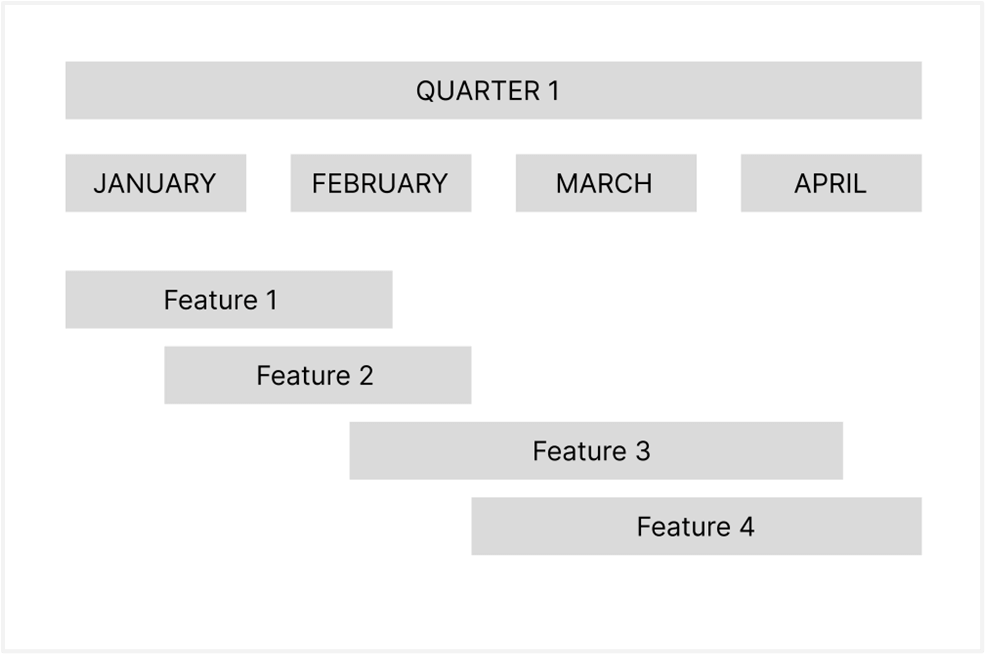
Agile roadmaps
In contrast, agile roadmaps are typically defined for a shorter time period. This is capable of being modified with additional changes that are critical. This makes it ideal for drastically changing market conditions. Software companies that follow agile methodology follow an Agile product roadmap. In KeyValue Software Systems, the Agile product roadmaps are mostly used for product development. It is one of the most followed roadmaps because of its flexibility. An agile roadmap gives the flexibility to change the duration and priority of a task/feature depending on the changing market conditions or in case of a change of plan by the team, depending on the decisions taken. An Agile product roadmap also has the flexibility to have tasks that can be initiated together, which do not have dependencies among them, based on the team's velocity and resources. An example of an agile roadmap can be found below.
How timeline flexibility changes based on the company stage
- Established companies may define roadmaps for 12 months or more
- Startups may work with 3 to 6 month roadmaps to validate ideas faster
Regardless of format, the goal is the same: build clarity, reduce uncertainty, and align the team.
Want to build smarter, faster, and more scalable digital products?
Explore how KeyValue’s product development team turns ideas into high-impact products. Let's talk!
Conclusion
Creating a successful product roadmap is not about predicting the future. It is about aligning vision, strategy, and execution in a structured, flexible manner. Whether you choose agile or waterfall, the key is continuous feedback, clarity, and adaptation.
A well-built roadmap becomes the backbone of your product development process.
FAQs
1. What is the first step in building a product roadmap?
Start by defining your product vision and the core problem you aim to solve.
2. How detailed should a software product roadmap be?
Internal roadmaps can be detailed, whereas external ones should remain simple and high-level.
3. What makes an agile product roadmap different?
Agile roadmaps are flexible, short-term, and allow parallel task execution based on team velocity.
4. How often should you update a product roadmap?
At least monthly. Fast-moving teams revise their roadmap every sprint.
5. What tools are best for product roadmap development?
Jira, Aha, Trello, Notion, and Productboard are widely used depending on team size and workflow.

